Are you interested in welding and want to pursue this profession? Do you love TIG welding and make an effort to learn about it? This is when you need them about TIG welding and its related information. You will probably start with the TIG welding setup for beginners first. We are ready to share with you!
What do you need to know when TIG Welding setup for beginners?
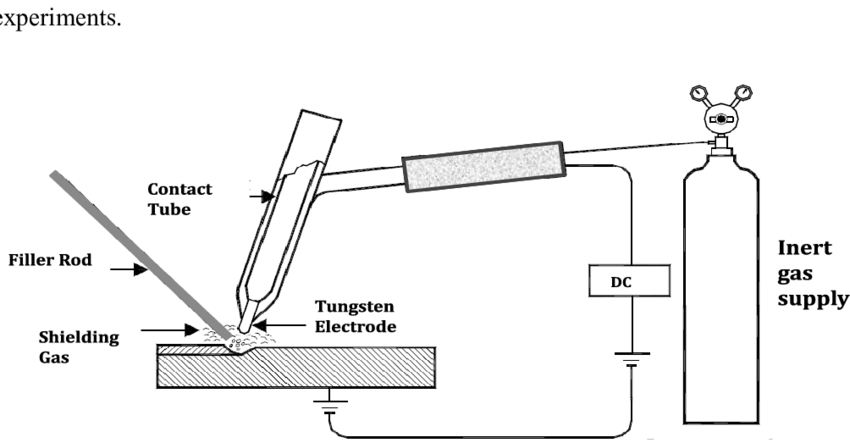
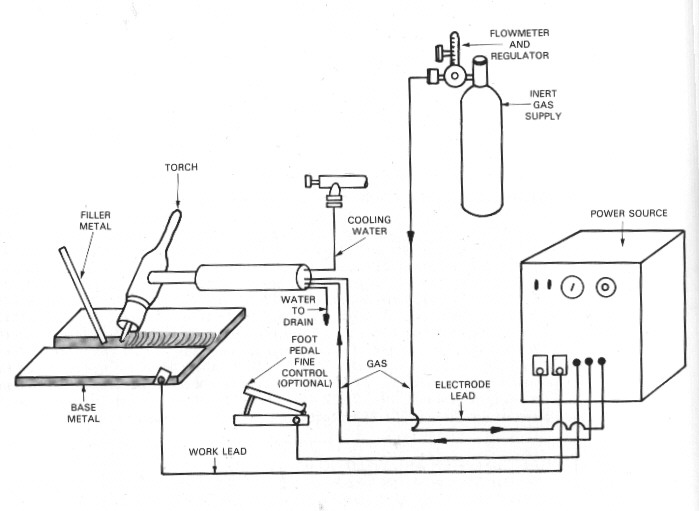
TIG welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a type of welding that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. Here is a basic setup for TIG welding:
1. Power source
The power source for TIG welding is a device that can deliver both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) power. It is typically a welding machine that can be adjusted to deliver the appropriate amperage and voltage for the specific TIG welding application.
AC power is used for welding aluminum and magnesium, while DC power is used for welding steel, stainless steel, and nickel alloys. The power source for TIG welding can be either a transformer-based machine or an inverter-based machine. Transformer-based machines are typically larger and heavier than inverter-based machines but are also more durable and have a longer lifespan.
It is essential that the power source is rated for the maximum amperage required for the welding process. High amperage welding requires a power source that is capable of delivering a high output. Many TIG welding power sources also have a built-in fan to keep the machine cool during operation, and it is important to make sure that the fan is functioning properly.
2. Tungsten electrode
Tungsten electrodes are the non-consumable elements used in TIG welding to produce the arc between the electrode and the workpiece. Tungsten has a high melting point (around 3,422 °C) and is a good conductor of electricity, which makes it suitable for use in TIG welding.
Tungsten electrodes come in a variety of sizes and types, and the choice of electrode will depend on the material you’re welding and the amperage range you’ll be using. The most common tungsten electrodes are:
- Pure Tungsten (Green)
- 2% Thoriated Tungsten (Red)
- 2% Ceriated Tungsten (Gray)
- 2% Lanthanated Tungsten (Gold)
- 1.5% Zirconiated Tungsten (White)
The diameter of the tungsten electrode is also important, a general rule of thumb is that the electrode should be about 1.5-2 times the thickness of the workpiece being welded. Also it’s important to use a clean and new electrode, it’s also good practice to grind the electrode to a fine point before starting the welding process.
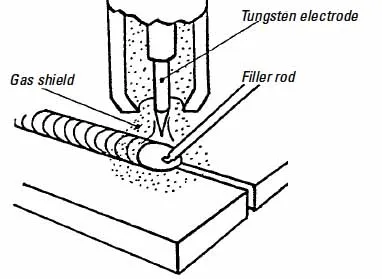
3. Welding torch
The welding torch is a device that delivers the shielding gas and the tungsten electrode to the workpiece in TIG welding (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding). A TIG welding torch typically consists of a body, a collet, a collet body, and a gas lens.
The body of the torch is the handle that the welder holds onto while welding. It is typically made of a heat-resistant material and has a switch or trigger that controls the flow of electricity to the electrode.
The choice of torch will depend on the amperage range you’ll be using and the thickness of the workpiece. TIG welding torches are available in different amperage ratings, and it is important to use a torch that is rated for the maximum amperage required for the welding process. The torch also needs to be comfortable to hold and easy to maneuver.
4. Filler metal
In TIG welding, filler metal is added to the weld pool as needed, in order to build up the weld and create a strong and continuous joint. The filler metal used in TIG welding should be the same or similar to the base metal in terms of composition and strength.
Filler metal for TIG welding is available in a variety of forms, including: Rods, Wire, Tapes. The type and size of the filler metal will depend on the welding application, the type of metal being welded, and the desired outcome.
It’s important to note that the filler metal should not be added too quickly to the weld pool, as this can lead to porosity (small bubbles) in the weld, and can also cause the weld pool to overflow and create excess spatter.
5. Gas supply
In TIG welding (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding), a shielding gas is used to protect the weld pool from contamination and provide a stable arc. The most common shielding gases used in TIG welding are argon and helium.
Argon is the most common shielding gas used in TIG welding, as it is relatively cheap and readily available. It provides a stable arc and good penetration, making it suitable for welding most metals, including steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Helium can be used with TIG welding when increased penetration and higher heat input are required, particularly when welding thicker sections or high-alloy metals, as it can be used at higher temperatures than argon. However, it is also more expensive and less readily available than argon.
6. Foot pedal or finger control
The amperage can be changed while TIG welding using a foot pedal or finger control. The amperage, also known as the welding current, controls the heat of the arc and the size of the weld pool.
A foot pedal is a device that is placed on the floor and is operated by the welder’s foot. It allows the welder to easily adjust the amperage while keeping both hands free to hold the torch. Foot pedals usually have a variable resistance, which allows the welder to adjust the amperage smoothly.
A finger control, also known as a thumb control, is a small hand-held device that the welder holds in one hand and uses their thumb to adjust the amperage. It allows for more precise control over the amperage and is more convenient for tight spaces and overhead welding.
Both foot pedals and finger controls are connected to the TIG welding power source and are used to adjust the amperage. The amperage can be increased or decreased by adjusting the position of the pedal or the thumb control.
Frequently asked questions (Weld FAQ)
What is the best type of TIG welding power source for a beginner?
For a beginner, it is recommended to start with a machine that is rated around 150-200Amp. This will allow you to practice on the same metal thickness and type before moving forward.
What is the best type of welding torch for a beginner?
For a beginner, it is recommended to start with a TIG welding torch that is rated for the amperage range you’ll be using and the thickness of the workpiece. It need to be convenient to handle and move around.
How do I choose the correct filler metal for my TIG welding project?
When choosing filler metal, it is important to select one that is the same or similar to the base metal in terms of composition and strength. It should also be compatible with the base metal and the shielding gas used, have the appropriate melting temperature for the base metal and the welding process, and be in a form that is easiest to use for the specific welding application.
Winding Up
In conclusion, TIG welding setup for beginners requires a good understanding of the welding process, the equipment, and safety precautions. It is important to choose the right TIG torch and accessories, set the correct amperage and polarity, and properly prepare the metal to be welded.
Always make sure to wear the appropriate personal protective equipment and follow all safety guidelines. Practice and patience are key to becoming proficient in TIG welding.