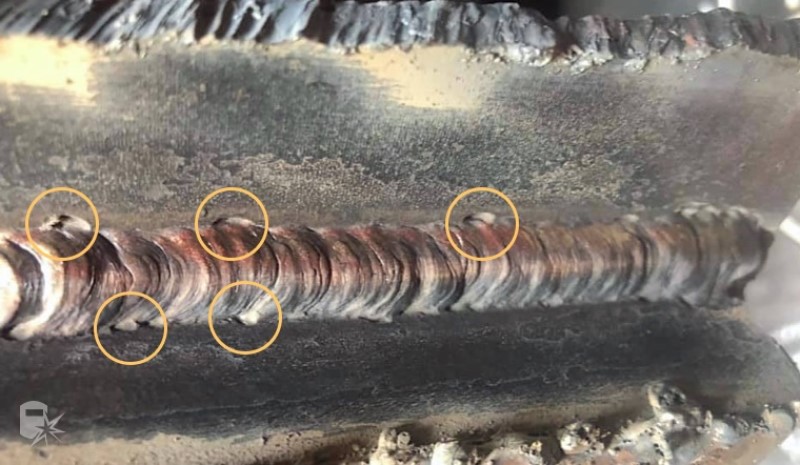
MIG welding is a common welding process that uses a wire electrode to form a weld between two pieces of metal. The process is simple and easy to learn, but there are a few things you can do to avoid cropping when MIG welding. Trimming is a weak point in a weld where the metal is not joined completely. Over time, the metal can slowly pull away from the weak spot, causing the weld to fail. So, how to avoid undercut in MIG welding? We have several ways we can help you in this blog!
What is undercut in welding?
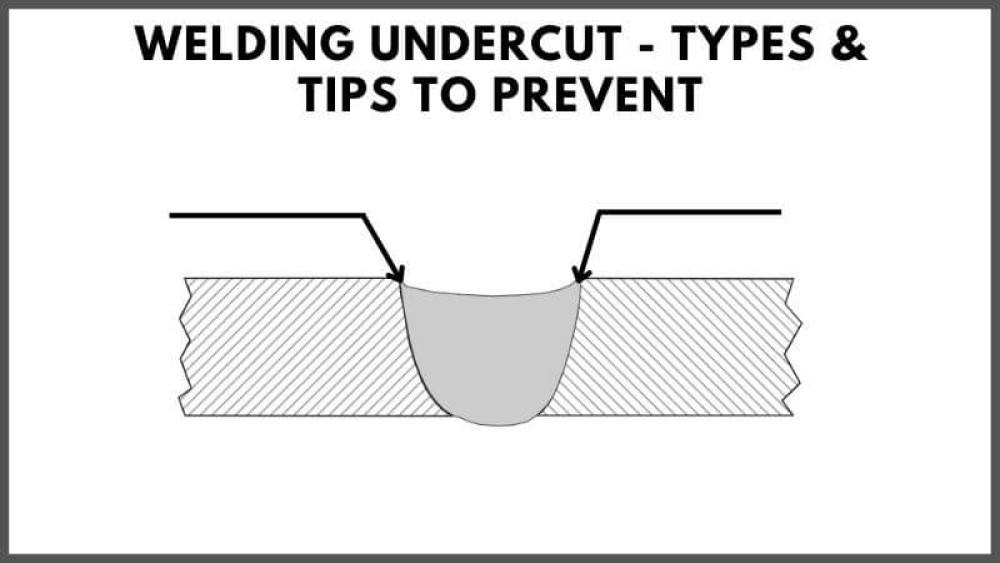
In welding, an undercut is a defect that occurs when the base metal is melted away along the edges of the weld, leaving a groove. This can weaken the structural integrity of the weld and potentially cause cracking or failure. An undercut is often caused by improper welding techniques, using a welding electrode that is too large, or having the welding speed set too high.
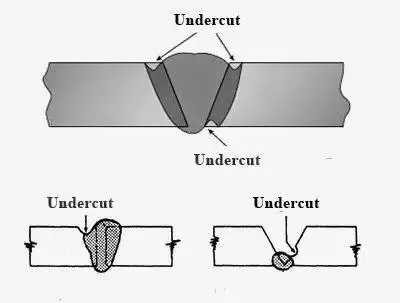
Types of undercut
1. Convex undercut
Convex undercut is a type of undercut in MIG welding where the weld bead is wider at the top than at the bottom, forming a convex shape. This type of undercut can cause weakness in the weld joint, reduce the overall strength of the weld, and make it more susceptible to cracking.
It can be caused by a variety of factors, including improper welding technique, incorrect welding parameters, or incorrect electrode selection. To avoid convex undercut, it is important to properly set the welding parameters, use the correct electrode, and maintain the correct welding technique.
2. Concave undercut
Concave undercut is a type of undercut in MIG welding where the weld bead is narrower at the top than at the bottom, forming a concave shape. This type of undercut can reduce the overall strength of the weld and make it more susceptible to cracking.
Concave undercut is often caused by a number of factors, including improper welding technique, incorrect welding parameters, or incorrect electrode selection. To avoid concave undercut, it is important to properly set the welding parameters, use the correct electrode, and maintain the correct welding technique.
3. V-shaped undercut
V-shaped undercut is a type of undercut in MIG welding where the weld bead forms a V-shape, with the point of the V at the bottom of the weld. This type of undercut can cause a reduction in the strength of the weld and make it more susceptible to cracking. It is often caused by welding too fast or using too much current, which can cause the molten metal to penetrate too deeply into the base metal.
To avoid V-shaped undercut, it is important to properly set the welding parameters, use the correct electrode, and maintain the correct welding technique. In addition, it is often helpful to increase the travel speed or decrease the current to reduce the penetration of the weld.

How to avoid undercut in MIG welding
Slow down your travel speed
Slowing down the travel speed can help to avoid undercut in welding, as it allows the molten metal more time to penetrate the base metal and helps to reduce the risk of undercutting. When welding too fast, the molten metal may not have enough time to properly penetrate the base metal, which can result in undercutting.
By slowing down the travel speed, you can ensure that the molten metal has sufficient time to penetrate the base metal and produce a strong, well-formed weld bead. It is important to find the optimal travel speed for each welding situation, as slowing down too much can also result in undercut or other weld defects.
To determine the best travel speed for a given situation, it is often helpful to experiment with different speeds and observe the resulting weld bead to find the speed that produces the best results.
Use the right filler metal
How to avoid undercut in MIG welding? Using the right filler metal can help to avoid undercut in MIG welding. The filler metal is used to add material to the weld pool and reinforce the weld. The choice of filler metal is important, as different filler metals have different properties that can affect the quality of the weld.
Factors to consider when choosing a filler metal include the type and thickness of the material being welded, the desired strength of the weld, and the required toughness and corrosion resistance. By choosing the right filler metal, you can ensure that the weld pool is properly reinforced and that the weld has the desired properties.
Additionally, using a filler metal with the correct melting temperature can help to prevent undercut, as the filler metal will melt at the same rate as the base metal and will not cool too quickly, which can cause undercutting.
Prevent contamination of the shielding gas
Preventing contamination of the shielding gas is an important step in avoiding undercut in MIG welding. Shielding gas is used to protect the weld pool from oxidation and contamination by the atmosphere. If the shielding gas becomes contaminated, it can cause the molten metal to react with the atmosphere, leading to porosity and other weld defects.
To prevent contamination of the shielding gas, it is important to use a high-quality shielding gas and to ensure that the shielding gas supply system is properly maintained and free of leaks.
Additionally, it is important to ensure that the shielding gas flow is adequate and that the gas is not blowing away from the weld pool. By preventing contamination of the shielding gas, you can help to ensure that the weld pool is properly protected and that the weld is free from defects.
Proper electrode selection
Proper electrode selection is an important step in avoiding undercut in MIG welding. The electrode is used to transfer the welding current to the workpiece and to provide filler metal for the weld.
The choice of electrode is important, as different electrodes have different properties that can affect the quality of the weld. Factors to consider when choosing an electrode include the type and thickness of the material being welded, the desired strength of the weld, and the required toughness and corrosion resistance.
Additionally, the electrode diameter should be chosen based on the thickness of the material being welded and the desired weld bead profile. By choosing the right electrode and maintaining the correct electrode angle, you can help to ensure that the weld pool is properly formed and that the weld has the desired properties.