In this blog post, we are going to discuss some of the most common welding mistakes people make. These mistakes can lead to less-than-optimal welds, which can eventually cause problems. So if you want to weld correctly make sure you know how not to weld the most common MIG welding mistakes. Let’s get started right now!
What are the most common MIG welding mistakes?
The most common MIG welding mistakes include Incorrect shielding gas, Improper joint preparation, Incorrect wire size and type, Improper welding technique, Not using the correct protective equipment, and more. Avoiding these common MIG welding mistakes can help ensure the weld will be strong, free of defects, and have a consistent and uniform bead profile. Why do I make bad welds?
How not to weld the most common MIG welding mistakes
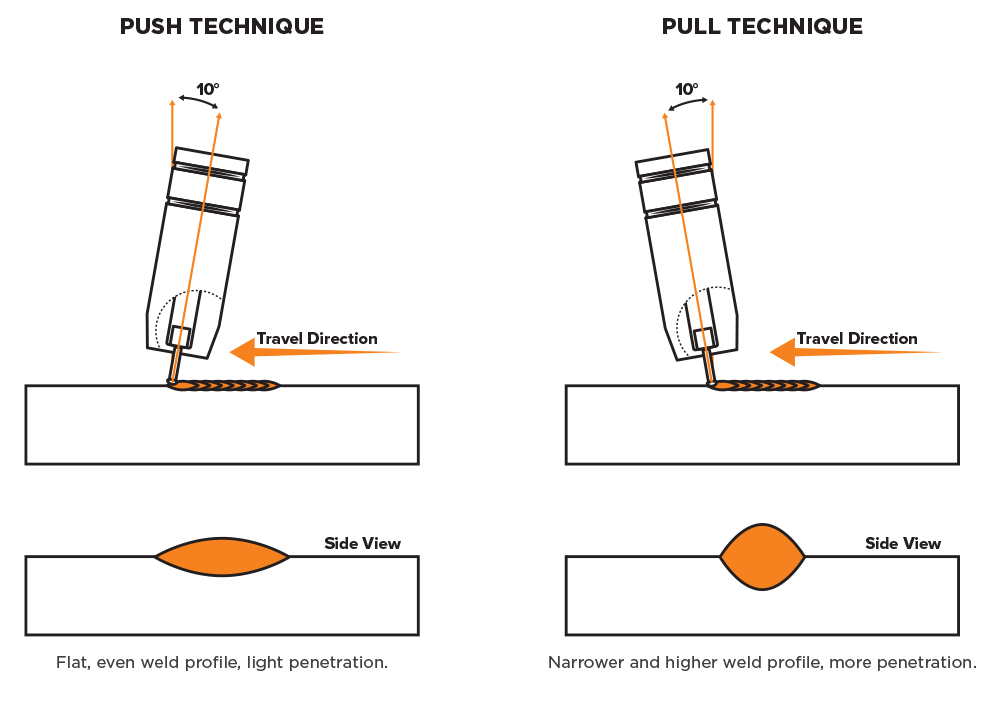
1. Use the proper welding technique
Using the proper welding technique is crucial in MIG welding for ensuring the quality and strength of the weld. The proper technique will vary based on the type of welding and the metal being welded.
It is important to practice and become proficient in the proper welding technique to ensure that the weld will be strong and free of defects. If the technique is not correct, the weld may be weak, porous, or prone to cracking, which can result in reduced joint strength and durability.
Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or a welding expert for the recommended welding technique for your specific application.
2. Use the correct shielding gas
Using the correct shielding gas is important in MIG welding to ensure the quality and integrity of the weld. Shielding gas protects the weld pool and surrounding metal from oxidation and other atmospheric contaminants that can weaken the weld and cause porosity.
When selecting a shielding gas, consider the following factors:
- Type of metal being welded: Different metals have varying requirements for shielding gases. For example, aluminum requires a shielding gas that is different from steel.
- Welding application: The type of welding application, such as welding in a flat, vertical, or overhead position, can affect the choice of shielding gas.
- Welding environment: The presence of wind, moisture, or other atmospheric contaminants can impact the choice of shielding gas.
Once the appropriate shielding gas has been selected, it is important to ensure that the gas flow is set correctly and that the gas is being delivered to the weld pool in an uninterrupted manner.
3. Choose the right wire size and type
Choosing the right wire size and type is important in MIG welding to ensure the quality and strength of the weld. The wire size and type should be selected based on the thickness of the metal and the desired strength of the weld.
- Wire size: The wire size should be chosen based on the thickness of the metal. A larger wire size is typically used for thicker metal, while a smaller wire size is used for thinner metal.
- Wire type: The wire type should be selected based on the type of metal being welded. For example, steel and stainless steel require different types of wire, and aluminum requires a specialized wire with a different composition.
It is important to choose the right wire size and type for the application to ensure that the weld will be strong and free of defects. If the wrong wire is used, the weld may be weak, porous, or prone to cracking, which can result in reduced joint strength and durability.

4. Set the voltage and wire feed speed correctly
Setting the voltage and wire feed speed correctly is important in MIG welding for ensuring the quality and strength of the weld. The voltage and wire feed speed control the heat input into the weld and the size of the weld bead, respectively.
Voltage: The voltage should be set high enough to produce a stable arc, but not so high that the metal overheats and warps. A common starting point for the voltage is around 20-22 volts for steel and stainless steel, and 14-16 volts for aluminum.
Wire feed speed: The wire feed speed controls the amount of filler metal that is added to the weld. The wire feed speed should be set fast enough to provide adequate filler metal, but not so fast that the metal overheats and warps. A common starting point for the wire feed speed is around 200-450 inches per minute (ipm).
5. Clean the metal surface
Cleaning the metal surface is a critical step in MIG welding to ensure the quality and strength of the weld. Dirt, oil, rust, or any other contaminants on the metal surface can weaken the weld, cause porosity, or result in a poor bead profile.
To clean the metal surface, you can use a wire brush, sandpaper, or degreaser to remove any contaminants. It is important to thoroughly clean the entire surface of the metal, including any corners, edges, and any other areas that will be welded.
Once the metal surface has been cleaned, it is important to handle the metal as little as possible to avoid re-introducing contaminants. If necessary, wear gloves to protect the metal from oil or other contaminants that may be present on your skin.
Properly cleaning the metal surface helps to ensure that the weld will be strong and free of defects, and that the bead profile will be consistent and uniform.

6. Prepare the joint
Proper joint preparation is crucial in MIG welding for ensuring the quality and strength of the weld. Proper joint preparation involves cleaning, fitting, and aligning the metal pieces to be welded.
- Clean the metal: Remove any dirt, oil, rust, or other contaminants from the metal surface. This can be done using a wire brush, sandpaper, or degreaser.
- Fit the metal pieces: Ensure that the metal pieces fit together tightly, with minimal gaps. If necessary, use clamps or welding magnets to hold the pieces in place.
- Align the metal pieces: Make sure that the metal pieces are properly aligned, so that the weld will be made in the strongest part of the joint.
Proper joint preparation helps to ensure that the weld will be strong and free of porosity. If the joint is not prepared correctly, the weld may be weak or porous, or the metal may warp or buckle during the welding process.
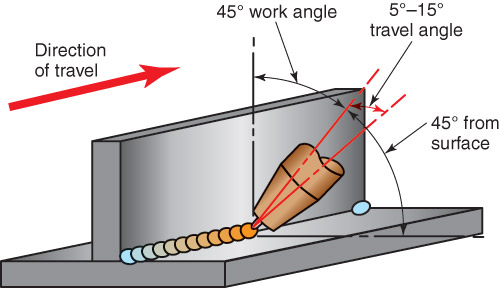
7. Weld at the proper angle
Welding at the proper angle is important for achieving a good bead profile and ensuring the strength and integrity of the weld. The proper angle will vary based on the type of welding and the metal being welded.
For example, in MIG welding, a travel angle of 5-15 degrees relative to the workpiece is common for a flat position weld. For a vertical or overhead position weld, a slightly steeper angle may be required.
It is important to maintain a consistent angle throughout the weld to ensure an even bead profile. If the angle is too steep, the weld bead can be too narrow and lack penetration. If the angle is too shallow, the weld bead can be too wide and have too much penetration, which can result in warping or buckling of the metal.
Wrapping Up
If you want to avoid welding mistakes, it is important to be aware of the most common ones. Make sure to practice regularly and take the time to learn the correct welding techniques. By following the guidelines in this article, you will know how not to weld the most common MIG welding mistakes.


